COMMUNICATION IN EVERYDAY LIFE ( Unit – 1 ) Theory of Communication || SEMESTER – 1
0
फ़रवरी 16, 2023
Verbal communication
Tags


%20Theory%20of%20Communication%20%20SEMESTER%20%E2%80%93%201.png)
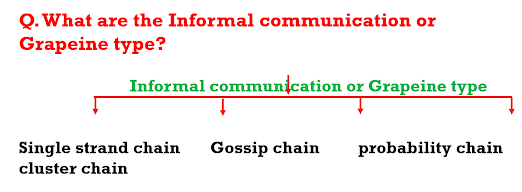


%20Theory%20of%20Communication%20%20SEMESTER%20%E2%80%93%201.png)

